Clustering Mixed Data Types in R
June 22, 2016Clustering allows us to better understand how a sample might be comprised of distinct subgroups given a set of variables. While many introductions to cluster analysis typically review a simple application using continuous variables, clustering data of mixed types (e.g., continuous, ordinal, and nominal) is often of interest. The following is an overview of one approach to clustering data of mixed types using Gower distance, partitioning around medoids, and silhouette width.
In total, there are three related decisions that need to be taken for this approach:
For illustration, the publicly available “College” dataset found in the ISLR package will be used, which has various statistics of US Colleges from 1995 (N = 777). To highlight the challenge of handling mixed data types, variables that are both categorical and continuous will be used and are listed below:
- Continuous
- Acceptance rate
- Out of school tuition
- Number of new students enrolled
- Categorical
- Whether a college is public/private
- Whether a college is elite, defined as having more than 50% of new students who graduated in the top 10% of their high school class
The code was run using R version 3.2.2 with the following packages:
set.seed(1680) # for reproducibility
library(dplyr) # for data cleaning
library(ISLR) # for college dataset
library(cluster) # for gower similarity and pam
library(Rtsne) # for t-SNE plot
library(ggplot2) # for visualizationBefore clustering can begin, some data cleaning must be done:
- Acceptance rate is created by diving the number of acceptances by the number of applications
- isElite is created by labeling colleges with more than 50% of their new students who were in the top 10% of their high school class as elite
college_clean <- College %>%
mutate(name = row.names(.),
accept_rate = Accept/Apps,
isElite = cut(Top10perc,
breaks = c(0, 50, 100),
labels = c("Not Elite", "Elite"),
include.lowest = TRUE)) %>%
mutate(isElite = factor(isElite)) %>%
select(name, accept_rate, Outstate, Enroll,
Grad.Rate, Private, isElite)
glimpse(college_clean)## Observations: 777
## Variables: 7
## $ name (chr) "Abilene Christian University", "Ad...
## $ accept_rate (dbl) 0.7421687, 0.8801464, 0.7682073, 0....
## $ Outstate (dbl) 7440, 12280, 11250, 12960, 7560, 13...
## $ Enroll (dbl) 721, 512, 336, 137, 55, 158, 103, 4...
## $ Grad.Rate (dbl) 60, 56, 54, 59, 15, 55, 63, 73, 80,...
## $ Private (fctr) Yes, Yes, Yes, Yes, Yes, Yes, Yes,...
## $ isElite (fctr) Not Elite, Not Elite, Not Elite, E...Calculating Distance
In order for a yet-to-be-chosen algorithm to group observations together, we first need to define some notion of (dis)similarity between observations. A popular choice for clustering is Euclidean distance. However, Euclidean distance is only valid for continuous variables, and thus is not applicable here. In order for a clustering algorithm to yield sensible results, we have to use a distance metric that can handle mixed data types. In this case, we will use something called Gower distance.
Gower distance
The concept of Gower distance is actually quite simple. For each variable type, a particular distance metric that works well for that type is used and scaled to fall between 0 and 1. Then, a linear combination using user-specified weights (most simply an average) is calculated to create the final distance matrix. The metrics used for each data type are described below:
- quantitative (interval): range-normalized Manhattan distance
- ordinal: variable is first ranked, then Manhattan distance is used with a special adjustment for ties
-
nominal: variables of k categories are first converted into k binary columns and then the Dice coefficient is used
- pros: Intuitive to understand and straightforward to calculate
- cons: Sensitive to non-normality and outliers present in continuous variables, so transformations as a pre-processing step might be necessary. Also requires an NxN distance matrix to be calculated, which is computationally intensive to keep in-memory for large samples
Below, we see that Gower distance can be calculated in one line using the daisy function. Note that due to positive skew in the Enroll variable, a log transformation is conducted internally via the type argument. Instructions to perform additional transformations, like for factors that could be considered as asymmetric binary (such as rare events), can be seen in ?daisy.
# Remove college name before clustering
gower_dist <- daisy(college_clean[, -1],
metric = "gower",
type = list(logratio = 3))
# Check attributes to ensure the correct methods are being used
# (I = interval, N = nominal)
# Note that despite logratio being called,
# the type remains coded as "I"
summary(gower_dist)## 301476 dissimilarities, summarized :
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.0018601 0.1034400 0.2358700 0.2314500 0.3271400 0.7773500
## Metric : mixed ; Types = I, I, I, I, N, N
## Number of objects : 777As a sanity check, we can print out the most similar and dissimilar pair in the data to see if it makes sense. In this case, University of St. Thomas and John Carroll University are rated to be the most similar given the seven features used in the distance calculation, while University of Science and Arts of Oklahoma and Harvard are rated to be the most dissimilar.
gower_mat <- as.matrix(gower_dist)
# Output most similar pair
college_clean[
which(gower_mat == min(gower_mat[gower_mat != min(gower_mat)]),
arr.ind = TRUE)[1, ], ]## name accept_rate Outstate Enroll
## 682 University of St. Thomas MN 0.8784638 11712 828
## 284 John Carroll University 0.8711276 11700 820
## Grad.Rate Private isElite
## 682 89 Yes Not Elite
## 284 89 Yes Not Elite# Output most dissimilar pair
college_clean[
which(gower_mat == max(gower_mat[gower_mat != max(gower_mat)]),
arr.ind = TRUE)[1, ], ]## name accept_rate
## 673 University of Sci. and Arts of Oklahoma 0.9824561
## 251 Harvard University 0.1561486
## Outstate Enroll Grad.Rate Private isElite
## 673 3687 208 43 No Not Elite
## 251 18485 1606 100 Yes EliteChoosing a clustering algorithm
Now that the distance matrix has been calculated, it is time to select an algorithm for clustering. While many algorithms that can handle a custom distance matrix exist, partitioning around medoids (PAM) will be used here.
Partitioning around medoids is an iterative clustering procedure with the following steps:
- Choose k random entities to become the medoids
- Assign every entity to its closest medoid (using our custom distance matrix in this case)
- For each cluster, identify the observation that would yield the lowest average distance if it were to be re-assigned as the medoid. If so, make this observation the new medoid.
- If at least one medoid has changed, return to step 2. Otherwise, end the algorithm.
If you know the k-means algorithm, this might look very familiar. In fact, both approaches are identical, except k-means has cluster centers defined by Euclidean distance (i.e., centroids), while cluster centers for PAM are restricted to be the observations themselves (i.e., medoids).
- pros: Easy to understand, more robust to noise and outliers when compared to k-means, and has the added benefit of having an observation serve as the exemplar for each cluster
- cons: Both run time and memory are quadratic (i.e., $O(n^2)$)
Selecting the number of clusters
A variety of metrics exist to help choose the number of clusters to be extracted in a cluster analysis. We will use silhouette width, an internal validation metric which is an aggregated measure of how similar an observation is to its own cluster compared its closest neighboring cluster. The metric can range from -1 to 1, where higher values are better. After calculating silhouette width for clusters ranging from 2 to 10 for the PAM algorithm, we see that 3 clusters yields the highest value.
# Calculate silhouette width for many k using PAM
sil_width <- c(NA)
for(i in 2:10){
pam_fit <- pam(gower_dist,
diss = TRUE,
k = i)
sil_width[i] <- pam_fit$silinfo$avg.width
}
# Plot sihouette width (higher is better)
plot(1:10, sil_width,
xlab = "Number of clusters",
ylab = "Silhouette Width")
lines(1:10, sil_width)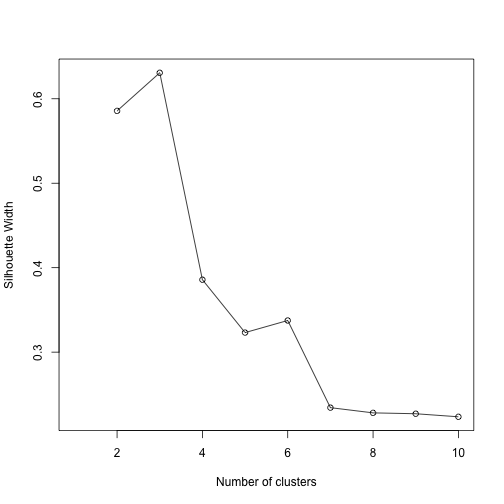
Cluster Interpretation
Via Descriptive Statistics
After running the algorithm and selecting three clusters, we can interpret the clusters by running summary on each cluster. Based on these results, it seems as though Cluster 1 is mainly Private/Not Elite with medium levels of out of state tuition and smaller levels of enrollment. Cluster 2, on the other hand, is mainly Private/Elite with lower levels of acceptance rates, high levels of out of state tuition, and high graduation rates. Finally, cluster 3 is mainly Public/Not Elite with the lowest levels of tuition, largest levels of enrollment, and lowest graduation rate.
pam_fit <- pam(gower_dist, diss = TRUE, k = 3)
pam_results <- college_clean %>%
dplyr::select(-name) %>%
mutate(cluster = pam_fit$clustering) %>%
group_by(cluster) %>%
do(the_summary = summary(.))
pam_results$the_summary## [[1]]
## accept_rate Outstate Enroll
## Min. :0.3283 Min. : 2340 Min. : 35.0
## 1st Qu.:0.7225 1st Qu.: 8842 1st Qu.: 194.8
## Median :0.8004 Median :10905 Median : 308.0
## Mean :0.7820 Mean :11200 Mean : 418.6
## 3rd Qu.:0.8581 3rd Qu.:13240 3rd Qu.: 484.8
## Max. :1.0000 Max. :21700 Max. :4615.0
## Grad.Rate Private isElite cluster
## Min. : 15.00 No : 0 Not Elite:500 Min. :1
## 1st Qu.: 56.00 Yes:500 Elite : 0 1st Qu.:1
## Median : 67.50 Median :1
## Mean : 66.97 Mean :1
## 3rd Qu.: 78.25 3rd Qu.:1
## Max. :118.00 Max. :1
##
## [[2]]
## accept_rate Outstate Enroll
## Min. :0.1545 Min. : 5224 Min. : 137.0
## 1st Qu.:0.4135 1st Qu.:13850 1st Qu.: 391.0
## Median :0.5329 Median :17238 Median : 601.0
## Mean :0.5392 Mean :16225 Mean : 882.5
## 3rd Qu.:0.6988 3rd Qu.:18590 3rd Qu.:1191.0
## Max. :0.9605 Max. :20100 Max. :4893.0
## Grad.Rate Private isElite cluster
## Min. : 54.00 No : 4 Not Elite: 0 Min. :2
## 1st Qu.: 77.00 Yes:65 Elite :69 1st Qu.:2
## Median : 89.00 Median :2
## Mean : 84.78 Mean :2
## 3rd Qu.: 94.00 3rd Qu.:2
## Max. :100.00 Max. :2
##
## [[3]]
## accept_rate Outstate Enroll
## Min. :0.3746 Min. : 2580 Min. : 153
## 1st Qu.:0.6423 1st Qu.: 5295 1st Qu.: 694
## Median :0.7458 Median : 6598 Median :1302
## Mean :0.7315 Mean : 6698 Mean :1615
## 3rd Qu.:0.8368 3rd Qu.: 7748 3rd Qu.:2184
## Max. :1.0000 Max. :15516 Max. :6392
## Grad.Rate Private isElite cluster
## Min. : 10.00 No :208 Not Elite:199 Min. :3
## 1st Qu.: 46.00 Yes: 0 Elite : 9 1st Qu.:3
## Median : 54.50 Median :3
## Mean : 55.42 Mean :3
## 3rd Qu.: 65.00 3rd Qu.:3
## Max. :100.00 Max. :3Another benefit of the PAM algorithm with respect to interpretation is that the medoids serve as exemplars of each cluster. From this, we see that Saint Francis University is the medoid of the Private/Not Elite cluster, Barnard College is the medoid for the Private/Elite cluster, and Grand Valley State University is the medoid for the Public/Not Elite cluster.
college_clean[pam_fit$medoids, ]## name accept_rate Outstate
## 492 Saint Francis College 0.7877629 10880
## 38 Barnard College 0.5616987 17926
## 234 Grand Valley State University 0.7525653 6108
## Enroll Grad.Rate Private isElite
## 492 284 69 Yes Not Elite
## 38 531 91 Yes Elite
## 234 1561 57 No Not EliteVia Visualization
One way to visualize many variables in a lower dimensional space is with t-distributed stochastic neighborhood embedding, or t-SNE. This method is a dimension reduction technique that tries to preserve local structure so as to make clusters visible in a 2D or 3D visualization. While it typically utilizes Euclidean distance, it has the ability to handle a custom distance metric like the one we created above. In this case, the plot shows the three well-separated clusters that PAM was able to detect. One curious thing to note is that there is a small group that is split between the Private/Elite cluster and the Public/Not Elite cluster.
tsne_obj <- Rtsne(gower_dist, is_distance = TRUE)
tsne_data <- tsne_obj$Y %>%
data.frame() %>%
setNames(c("X", "Y")) %>%
mutate(cluster = factor(pam_fit$clustering),
name = college_clean$name)
ggplot(aes(x = X, y = Y), data = tsne_data) +
geom_point(aes(color = cluster))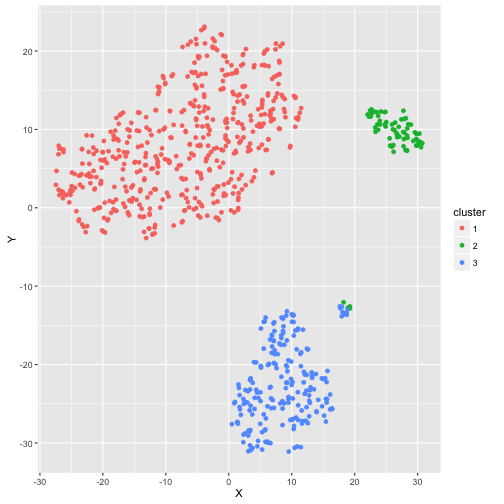
By investigating further, it looks like this group is made up of the larger, more competitive public schools, like the University of Virginia or the University of California at Berkeley. While not large enough to warrant an additional cluster according to silhouette width, these 13 schools certainly have characteristics distinct from the other three clusters.
tsne_data %>%
filter(X > 15 & X < 25,
Y > -15 & Y < -10) %>%
left_join(college_clean, by = "name") %>%
collect %>%
.[["name"]]## [1] "College of William and Mary"
## [2] "Georgia Institute of Technology"
## [3] "SUNY at Binghamton"
## [4] "SUNY College at Geneseo"
## [5] "Trenton State College"
## [6] "University of California at Berkeley"
## [7] "University of California at Irvine"
## [8] "University of Florida"
## [9] "University of Illinois - Urbana"
## [10] "University of Michigan at Ann Arbor"
## [11] "University of Minnesota at Morris"
## [12] "University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill"
## [13] "University of Virginia"A Final Note: Dealing with Larger Samples and One-Hot Encoding
Because using a custom distance metric requires keeping an NxN matrix in memory, it starts to become noticeable for larger sample sizes (> 10,000 or so on my machine). For clustering larger samples, I have found two options:
- Two-step clustering in SPSS: This model-based clustering approach can handle categorical and continuous variables and utilizes silhouette width (using rule-of-thumb cutoffs) to find the optimal number of clusters.
- Using Euclidean distance on data that has been one-hot encoded: While much quicker computationally, note that this is not optimal as you run into the curse of dimensionality fairly fast since all categoricals are recoded to become sparse matrices. Note that this approach is actually fairly similar to the dice coefficient found in calculation of Gower distance, except it incorrectly labels 0-0 as a match. More on this can be seen in this discussion.
